View count:
3944
I. Goals, core competencies and courses
Item 1:Goals, core competencies and courses
1-1Educational objectives and core competencies of the class system and their developmentThis department is based on the humanistic spirit of the school's creation, practical application-oriented, combined with information technology and digital learning. Its purpose is to cultivate information system management and development, network and multimedia production, Digital content design and early stage talents for animation and game production; master's and master's in-service classes are designed to nurture research and management talents in information systems, internet and multimedia, and learning and digital technologies.
The educational objectives of the department are to meet the educational objectives of the school and the hospital, to analyze the current situation and prospects of the relevant fields and the development of the job market, as well as to assess the characteristics and positioning of students, and to develop consensus through previous departmental meetings and departmental curriculum committees. The part of the review and amendment mechanism is mainly promoted through a system of formal administrative operations, including departmental meetings, departmental curriculum committees, teaching evaluations, academic meetings, academic course committees, school meetings, school curriculum committees, and departments. , school, school self-assessment, etc. In addition, the department also provides feedback and improvement mechanisms through informal administrative channels such as departmental associations, departmental associations, departmental seminars, and questionnaires. The following is a further explanation of the educational goals in accordance with the educational goals of the school and the hospital, the development status and prospects of the job market, the characteristics and positioning of students, and the conditions of teachers.
The relationship between the educational goals of the school and the school and the educational goals of the university. Foguang University is based on the humanistic spirit and implements the three life concepts of life, life and career. The purpose of its establishment is to cultivate a socially strong talent with both character, quality and taste. . As for the School of Creativity and Technology, combining cultural assets and creativity, information applications, product and media design and communication, the aim is to cultivate: (1) professionals in cultural creativity and technology communication, and (2) promotion of cultural and creative industries. The development of talents, (3) the professional ethics, the talents of social responsibility, and (4) the cultivation of creative thinking, design and development of talents, the educational goals of the department and the goals of the school and the hospital are very compatible, the education of the school and the school For the target, please see [Appendix 2-1-1].
The development of the employment market and its prospects are related to the educational goals. The Executive Yuan announced the six emerging industries in China in May 1998, and under the “Creative Taiwan – Cultural and Creative Industry Action Plan”, the economy The Ministry of Planning has developed a "Clan Content Industry Development Action Plan" to promote the development of the niche content industry through a combination of government policies and private resources with a more focused focus on regional development strategies and action plans. As for the implementation of the project, the four projects, including the "Industry Development Leap Forward Project", the "Civil Content Institute Project", the "International Air Navigation Expansion Project", and the "Study Programme and Collection Project" are the key projects. In the above-mentioned industrial development policies formulated by the government, the "數" content is very suitable for combining with the rich cultural style and sightseeing and leisure resources possessed by the Yilan area. Under the current well-established communication network infrastructure, actively cultivate multimedia digital content technology talents. It will certainly lay a good foundation for the development of the digital content industry in the eastern Taiwan region. The National Science Foundation "Zhuke Yilan Base" has been completed and is planned to be a "Communication Knowledge Service Park" with an area of 73 hectares. The project is based on software design and communication industry manufacturers. It is conceivable that in the future, Yilan's industrial development will be based on high-tech, pollution-free communication technology and software design industry. In this regard, the department will cooperate with the government's industrial policy and actively counsel the academic circles and manufacturers to establish digital numbers in the Lanyang area. The Content Technology R&D Center believes that the teachers of this department can cultivate talents with both theory and practice, create a new opportunity for industrial development in East Taiwan, and achieve a win-win situation in which environmental protection and industry coexist.
In September of the 100th year of the Republic of China, Zhang Zhongmou, chairman of TSMC, outlined the future of science and technology in the summit held by the Taiwan Semiconductor Industry Association. He believes that smart phones, tablets and e-books will drive the future "golden for another decade". . In addition, with the rapid development of mobile communication technology, the innovation of smart phones and the popularity of mobile Internet access, the mobileization of digital content should be the development direction of future mobile device value-added. According to market research firm Newzoo, the number of global games in the Republic of China exceeded 1.7 billion in 103 years, and the market size reached $81.5 billion. As for the number of digital games in Taiwan, according to Nielsen's 2014 survey, there are at least 7.45 million people. According to the statistics of the Industrial Bureau, it has reached NT$45.32 billion in 2013. However, China's game market is at a mature stage, in order to occupy in a highly competitive market. In one place, the Ministry of Economics listed games as an important driving item for the knowledge economy, and encouraged the development of game software combined with software engineering and video sound technology to enable the industry to upgrade smoothly. In this regard, the department will focus on the development of stereo animation, graphics technology and audio and video recognition, and the design of game software that can be executed on different platforms.
The Yilan area is rich in humanities, rich in cultural relics, and the birthplace of many folk operas. In addition to its unique geographical environment, there are many cultural relics worthy of collection and sharing with the world. It should be promoted and utilized. Yilan Science Park is the first science park to focus on the development of knowledge economy (including communication knowledge, cultural creativity, digital content, research and development, etc.). After the emerging knowledge service industry has entered, the existing Neihu Science and Technology Park can be connected. The Nangang Software Industrial Park will form an industrial cluster effect and combine with the local sightseeing and tourism service industry in Yilan to drive more business opportunities and employment opportunities. The Yilan County Government has further proposed the development axis of “Information County”, “Technology County, University City” since the introduction of “Environmental Protection County” and “Tourism County” and “Cultural County”. The school is located at the northern end of the Lanyang area. It has established a profound relationship with Yilan for more than a decade. In addition to the many Yilan students, the social responsibility and social care of the university itself have also prompted the teachers and students to participate in many Yilan areas. Various types of research projects and activities have made the teachers and students of the school not only have an in-depth understanding of the Yilan area, but also paid a deep concern for the Yilan area. In order to integrate the knowledge and skills of the upper, middle and lower reaches of the cultural and creative industries, the School established the School of Creativity and Technology in the 100th academic year, which is divided into four departments: cultural assets and creativity, information applications, product and media design and communication. Committed to the development of the school's cultural creativity / digital content industry research and development features, I hope that cultural creativity / digital content can become a starting point for the country to re-recognize the school. Since the beginning of the 99th year, the department has implemented a number of programs led by the Ministry of Education. These programs help students to accumulate digital content development and design experience, and strengthen students' ability to integrate applications, which in turn allows them to move toward action. Specialized areas such as device App, Internet and mobile content and digital content design.
Evaluating the relationship between student traits and orientation and educational goals. The sources of university students are mostly graduates of ordinary high school (or equivalent), and a small number of them belong to the technical system (such as four skills, two specialties or higher vocational posts). The graduates are either enrolled in the department through different channels such as transfer examination, transfer, and credit classes. However, with the popularity of integrated high schools, the boundaries between ordinary high schools and vocational schools are becoming blurred, and the sources of students are increasingly diversified. As far as the academic orientation of students is concerned, most of the students in this department belong to the second group (ie, the science and engineering group). However, since the 100 years of the department and the Department of Learning and Digital Science and Technology, the first group (That is, the proportion of students in the grammar business group) has increased significantly. In order to respond to this change, the curriculum, teaching content and teaching methods of the department are bound to make major amendments in response to this change. As far as the professional background of the students is concerned, the freshmen of this department generally do not have the basic knowledge of computers when they enter the school. However, most of the students are familiar with the operation of the computer and the use of popular application software (for example: MS Office, mobile application App Etc.), and very keen on playing online and mobile games, a small number of students who receive technical education and training, already have considerable experience in computer practice, and get multiple licenses for basic computers (eg TQC, etc.) . Therefore, how to bring students with different academic degrees and different levels into the same classroom, the curriculum design must pay attention to the basic needs of these students, and the teaching methods must also be changed in time to achieve the pre-set educational goals and cultivate The professional competence of the students.
In terms of students' willingness to learn and motivation, the motivation and willingness of the university students are generally low, and the sense of achievement of the students is generally low. The freshmen's entrance interviews show that the students have to take courses for the university for four years. I don’t know much about it. For the professional content of this course, I only stay in the superficial and superficial cognition. However, this phenomenon is common among domestic colleges and universities, and is not caused by a single factor (for example, poor degree or enrollment). The score is too low, etc.), but the dilemma that arises in the overall development of society. Perhaps how to guide students' concepts in the university within four years and establish a correct attitude towards learning is a more important topic besides professional content.
The undergraduate and master's in-service students of this department are mainly from primary and secondary school teachers in Lanyang and nearby areas, information related personnel in public and private institutions, recent graduates of universities and colleges in the department and neighboring regions, and the general public. These students have a lot of differences in theoretical knowledge and practical skills in the application of information. Many students are limited in their ability to participate in learning because of their full-time students. However, these students are proactive and understand well. It is a professional field that is familiar to them, and can discuss the experience in a clear and orderly way. In recent years, due to factors such as the overall economic weakness, low wages, and low employment, the undergraduate and master's in-service students have suffered from the same sources as other schools.
Relevance of teacher qualifications and educational goals In addition to the above factors, the conditions of the teachers are still needed to determine the educational goals of the department. In addition to a small number of concurrent teachers, the department has a Ph.D., and research expertise is also in the field of information applications. The Department divides teachers into several related fields through the concept of grouping by course, and formulates corresponding educational goals. For the grouping of teachers' expertise, please see [Appendix 2-1-2]. This approach can avoid the empty educational goals, but the teachers can not achieve the dilemma, the group can know that the department's teacher conditions and the educational goals set up have a very high correlation, enough to support the university, the university Master's and Master's in-service specializations with different expertise.
Education Objectives, Student Professional/Core Competence, and Learning Competency Indicators The following is a comprehensive description based on the educational goals set by the above factors, the professional/core competencies that students need to have, and the learning ability indicators that determine whether core competencies are achieved. Considering the employment prospects and the quality and interest of students, the four university programs provided by the department cover several popular areas, among which "information system and management" and "network and multimedia" are more suitable for the physical engineering group. The "Digital Content Design" is more suitable for students who are suitable for the grammar business group. The "Animation and Game Design" covers creative design, multimedia content production, programming, game scripting, etc., suitable for science and engineering and grammar business. The participation of students of the attribute is no longer limited to the traditional binary or taxonomic classification of the literary group or the science and technology, but also more consistent with the current concept of cross-domain learning.
[Table 2-1-1] The learning ability indicators for the professional/core competence and testing professional competence of each department of the Department. For the department, having the basic information science, practical development, and the ability to cooperate and communicate with others is the basic ability that should be possessed by the information technology first-time personnel, so these skills are classified as the core/professional/core competence. The learning ability is reflected in the writing of the program, the interpretation of the basic theory of information science, and the communication and cooperation with the team members and the completion of the thematic implementation. The other courses of the department set the professional/core competence of the students, focusing on the application of theory into practical operations, rather than focusing on the verification and development of the theory. The educational goals of this department are closely related to the educational goals of the school and the school. Although [Table 2-1-1], the indicators related to information professional ethics and social services are not included, but in the course of the course, the general course of the school There are a number of related courses, even cross-disciplinary cultural creative implementation courses, which can cultivate students' correct professional ethics and social service spirit in addition to professional competence. For students with low motivation and willingness to learn, Positive, positive encouragement and inspiring role, this is the best example of the Department's response to the basic spirit of the people-centered creation of Fo Guang University and the promotion of the "righteousness and morality" principle of conduct.
The education objectives of the master's and master's in-service classes are to cultivate information systems, internet and multimedia, and research and management talents in learning and digital technology. For their professional/core competencies and learning ability indicators, please see [Table 2-1- 2] and [Table 2-1-3]. There are obvious differences between the three groups of students in the master's and master's in-service classes, but the department believes that students should be able to integrate the theories and skills related to their research, independently implement their own research, and have development, management and evaluation. The ability of the information system. It is worth noting that the professional/core competence of the master's and master's in-service classes is the same, but the latter is used to verify the achievement of the core competence, and pays more attention to the link between theory and research and the practical work of the in-service learners.
[Table2-1-1]:大學部專業/核心能力與其相對應之學習成效指標
[表2-1-2]:碩士班專業/核心能力與其相對應之學習成效指標
[表2-1-3]:碩士在職班專業/核心能力與其相對應之學習成效指標
| 專業/核心能力 | 學習成效指標 |
| 1. 系核心學程:具備基礎資訊科學、實務開發以及合作與溝通的能力 |
l 能以電腦程式語言撰寫程式 l 能闡述資訊科學基礎理論 l 能與團隊成員進行溝通合作並完成專題實作 |
| 2. 資訊系統與管理學程:具備資訊系統分析、設計、管理與開發的能力 |
l 能開發網頁資訊系統 l 能開發嵌入式系統 l 能分析、設計與管理資訊系統 |
|
3. 網路與多媒體學程:具備網路與多媒體系統開發的能力 |
l 能設計與開發多媒體系統 l 能分析與開發行動裝置系統 l 能維護與管理網路系統 |
|
4. 數位內容設計學程:具備數位內容設計與製作的能力 |
l 能應用數位多媒體之設計與製作原則 l 能應用系統化教學設計的要素 l 能應用數位多媒體評鑑方法與原則 |
| 5. 動畫與遊戲設計學程:具備動畫與數位遊戲設計與開發的能力 |
l 能設計與製作動畫 l 能設計與製作數位遊戲 l 能企劃與撰寫遊戲腳本 |
[表2-1-2]:碩士班專業/核心能力與其相對應之學習成效指標
| 專業/核心能力 | 學習成效指標 |
|
具備資訊系統與管理之研究與管理能力 |
l 能整合資訊應用相關的理論與技能 l 能執行資訊應用相關的研究 l 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 |
| 具備網路與多媒體之研究與管理能力 |
l 能整合資訊應用相關的理論與技能 l 能執行資訊應用相關的研究 l 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 |
|
具備學習與數位科技之研究與管理能力 |
l 能整合資訊應用相關的理論與技能 l 能執行資訊應用相關的研究 l 能開發、管理與評鑑數位教材或資訊系統 |
[表2-1-3]:碩士在職班專業/核心能力與其相對應之學習成效指標
| 專業/核心能力 | 學習成效指標 |
|
具備資訊系統與管理之研究與管理能力 |
l 能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能 l 能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究 l 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 |
| 具備網路與多媒體之研究與管理能力 |
l 能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能 l 能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究 l 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 |
|
具備學習與數位科技之研究與管理能力 |
l 能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能 l 能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究 l 能開發、管理與評鑑數位教材或資訊系統 |
1-2 The Curriculum Planning of Class and Its Relationship with Educational Objectives and Core Competence
The first section of this sub-project will explain the relationship between the curriculum design of the bachelor class and the set educational goals and professional competence. The second section will describe the curriculum planning and the set educational goals and majors of the master's and master's in-service classes. The correlation between capabilities.
1-2-1The relationship between the curriculum planning of bachelor classes and its educational goals and core competencies
Since the 101st school year, under the leadership of Yang’s President Chao Xiang, the University Department has fully implemented the course of study. The purpose of the school is to make the learning effect more clear. In addition to strengthening the core knowledge of the subject area, the graduate credits are still maintained at least. Under the premise of 128 credits, it can cover more than 20 credits, and students can freely use them according to individual interests or combined with career planning, and also increase the space for cross-disciplinary learning. In this way, students from different fields and different sexual orientations can freely choose appropriate courses according to their own background, abilities and interests, and meet the requirements of 128 credits, which increases the flexibility of choice. Students with different needs can get what they want. Under the curriculum of the academic program, the complex courses of the traditional departments and the re-arrangement of the emerging disciplines, in order to seek systematic and solid subject knowledge education, remove the anachronistic curriculum, and divide the basic scholastic into different stages of the course, such as Basic courses, core courses, professional courses, etc., are clearly structured to meet the needs of individualization. The advantages of the program system in the new century society facing a high degree of continuous division of labor are far beyond the curriculum design of the traditional department. Specifically, mobility, flexibility and cross-domain integration are different from the old ones. The biggest feature of the credit system, and the diverse selection of courses can also lead students to think about what they should actively learn and give students a truly free and self-responsible learning environment.
In order to cultivate the four types of talents mentioned in the former sub-project, the bachelor's degree program specially plans a core course and four professional elective courses, taking into account the characteristics of students' diverse sources and more suitable for image-based learning. The curriculum content is oriented towards diversity, adaptability and practical application. The curriculum structure is based on basic introduction, advanced and integrated application. Each grade has a learning focus, and the allocation of compulsory and elective courses is also appropriate. In addition to the program examinations, the Department will also use the assessment criteria to provide students with a clearer basis for their understanding of the integrated application skills of the students through basic thematic implementation and thematic implementation. The professional/core competencies and learning effectiveness indicators of the various programs of the department and their corresponding courses are listed in [Table 2-1-4] to [Table 2-1-8].
[Table 2-1-4]:Undergrate class "core program" learning achievement indicators and curriculum association
|
專業/核心能力:具備基礎資訊科學、實務開發以及合作與溝通的能力 說明:訓練學生具備資訊科學領域之基礎學理和技術原理與應用的專業知能,理論與實務並重,以便日後能藉以學習更進階之知識與技能。另透過專題實作課程,以培養專案開發所需之有效溝通與團隊合作的能力。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能以電腦程式語言撰寫程式 | 程式設計、資料結構、資料庫系統、基礎專題實作1、基礎專題實作2、專題實作1、專題實作2 |
| 能闡述資訊科學基礎理論 | 計算機概論、微積分、系統分析與設計、資料通訊與電腦網路、資料庫系統、基礎專題實作1、基礎專題實作2、專題實作1、專題實作2 |
| 能與團隊成員進行溝通合作並完成專題實作 | 溝通與簡報技巧、基礎專題實作1、基礎專題實作2、專題實作1、專題實作2、實務實習 |
[表2-1-5]:學士班「資訊系統與管理學程」學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備資訊系統分析、設計、管理與開發的能力 說明:學生需對資訊系統的分析與設計有一基礎認識,並能實際管理與實作開發一資訊系統。其中,資料庫管理、離散數學及系統分析與設計課程讓學生對資訊系統的架構有一基礎認識,程式設計課程則讓學生學得實際開發能力,管理資訊系統、決策支援系統及人工知慧則讓學生能更有效運用資訊系統進行資訊運用及管理。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能開發網頁資訊系統 | 計算機數學、離散數學、互動式網頁製作、演算法、網頁程式設計、進階網頁程式設計 |
| 能開發嵌入式系統 | 計算機數學、人機互動程式設計、離散數學、嵌入式程式設計、演算法、智慧型代理人 |
| 能分析、設計與管理資訊系統 | 智慧型代理人、進階網頁程式設計、管理資訊系統、決策支援系統、人工智慧概論 |
[表2-1-6]:學士班「網路與多媒體學程」學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備網路與多媒體系統開發的能力 說明:學生需對影像、聲音、視訊與網路的基本原理有一基礎之認識,並能夠結合計算機的軟硬體進行網路系統與多媒體的管理與應用。其中基礎科目如計算機數學、離散數學為培養網路與多媒體的基礎知識,而程式設計的相關課程則培養學生的實作能力。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能設計與開發多媒體系統 | 計算機數學、物件導向程式設計、離散數學、影像處理概論、多媒體系統 |
| 能分析與開發行動裝置系統 | 計算機數學、物件導向程式設計、離散數學、行動裝置程式設計、進階行動裝置程式設計 |
| 能維護與管理網路系統 | 計算機系統、作業系統、無線網路概論、網路管理、網路程式設計 |
[表2-1-7]:學士班「數位內容設計學程」學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備數位內容設計與製作的能力 說明:學生需對數位學習、數位遊戲、數位影音與數位出版等相關領域(產業)有一基礎之認識,擁有學習與多媒體設計之理論知識,以及具備企劃、設計、製作與評鑑教育類和非教育類數位多媒體專案之能力以因應職場需求。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能應用數位多媒體之設計與製作原則 | 學習科技與多媒體概論、數位影音編輯、數位學習概論、多媒體企劃與腳本實作、遊戲開發與腳本實作、數位出版實作、兒童遊戲設計、數位內容評鑑、課程開發與學習平台管理 |
| 能應用系統化教學設計的要素 | 數位出版實作、兒童遊戲設計、數位教學設計、線上課程帶領方法與技巧、數位內容評鑑、課程開發與學習平台管理 |
| 能應用數位多媒體評鑑方法與原則 | 學習科技與多媒體概論、數位影音編輯、數位學習概論、多媒體企劃與腳本實作、遊戲開發與腳本實作、數位出版實作、兒童遊戲設計、數位教學設計、線上課程帶領方法與技巧、數位內容評鑑、課程開發與學習平台管理 |
[表2-1-8]:學士班「動畫與遊戲設計學程」學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備動畫與數位遊戲設計與開發的能力 說明:設計尖端、具吸睛效果的動畫應用系統(含數位遊戲)所須具備的技術能力為動畫與遊戲系統成功的一重要環節,而其內容則包括:平面/3D動畫設計技術、平面/3D動畫程式設計、以及尖端的資料輸入技術如影像辨識和體感技術等。除上述技術能力外,企劃能力亦是成功應用的另一重要環節,此均為動畫與數位遊戲設計與開發的重要能力。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能設計與製作動畫 | 視窗程式設計、2D動畫製作、影音辨識概論、3D動畫設計與製作、2D動畫程式設計、人工智慧概論 |
| 能設計與製作數位遊戲 | 視窗程式設計、2D動畫製作、影音辨識概論、互動遊戲設計、3D動畫設計與製作、2D動畫程式設計、3D遊戲程式設計、3D遊戲製作、人工智慧概論、軟體工程概論 |
| 能企劃與撰寫遊戲腳本 | 互動遊戲設計、遊戲企劃與腳本實作、3D遊戲製作 |
值得說明的是,本系在設計課程時,先由全體專任教師透過系課程委員會議,溝通討論系核心學程之專業/核心能力以及必修與選修科目,其它學程之專業/核心能力與科目內容,則由學程召集人與具相關專長之專任教師開會擬定後,再送至系課程委員會通過後施行。有關本系學士班各學程之專業/核心能力以及科目之制定過程,請見[附錄2-1-2]之系課程會議紀錄以及[附錄2-1-3] 之大學部課程大綱,至於在實施學程化課程後,各科目之開課次數紀錄,請見[附錄2-1-4]。而學士班課程地圖如[圖2-1-1]所示。
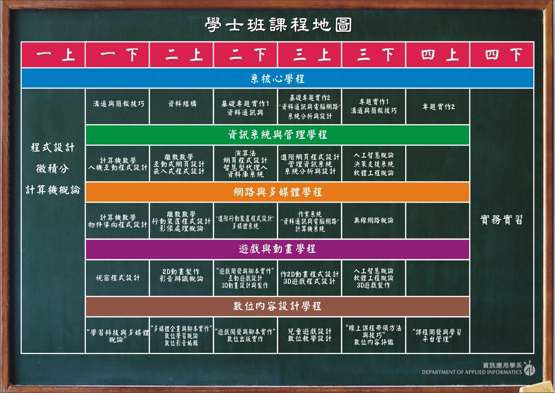
[圖2-1-1]:本系學士班課程地圖
1-2-2 The relationship between the curriculum of master's and master's in-service special courses and its educational goals and core competence
The master's and master's in-service classes in this department are provided with information systems and management, network and multimedia, and learning and squatting technology. In order to respond to and develop a variety of master's and master's students, they will be provided under each group since the 103th school year. Six modular courses, namely, information systems and management, including two modules for the development and application of intelligent information applications and information systems. The network and multimedia groups include two modules of innovative network and multimedia technology, as well as learning. The Digital Technology Group consists of two modules for learning and e-government. In addition to the compulsory courses in the "Information Application Panel Discussion", students can freely choose modules or freely combine the appropriate courses to complete their studies according to their research interests and career planning. The professional/core competencies and learning effectiveness indicators of the six modules and their corresponding courses are listed in [Table 2-1-9] to [Table 2-1-14].
The master's and master's in-service classes in this department are provided with information systems and management, network and multimedia, and learning and squatting technology. In order to respond to and develop a variety of master's and master's students, they will be provided under each group since the 103th school year. Six modular courses, namely, information systems and management, including two modules for the development and application of intelligent information applications and information systems. The network and multimedia groups include two modules of innovative network and multimedia technology, as well as learning. The Digital Technology Group consists of two modules for learning and e-government. In addition to the compulsory courses in the "Information Application Panel Discussion", students can freely choose modules or freely combine the appropriate courses to complete their studies according to their research interests and career planning. The professional/core competencies and learning effectiveness indicators of the six modules and their corresponding courses are listed in [Table 2-1-9] to [Table 2-1-14].
[表2-1-9]:Learning effectiveness indicators and course association tables for the "Smart Information Application" module course for master's and part-time master's classes
|
專業/核心能力:具備資訊系統與管理之研究與管理能力 說明:學生需要對於目前巨量資料(Big Data)環境下的資訊管理和智慧型決策分技術之發展趨勢進行瞭解。所探討主題包括:資料工程、資料庫、資料模式與知識探索、人工智慧、管理資訊系統、智慧型決策支援系統等內容,並且能夠利用上述的技術為工具解決巨量資料之商業智慧與決策支援的實務應用與研究中所面對的問題。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
|
能整合資訊應用相關理論與技能(能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能) |
資料工程、資料模式與知識探索、智慧型決策支援系統、人工智慧專題、管理資訊系統專題、群集智慧、高等資料庫、財務運算、網頁擷取程式設計 |
| 能執行資訊應用相關研究(能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究) | 資料工程、資料模式與知識探索、智慧型決策支援系統、人工智慧專題、管理資訊系統專題、群集智慧、高等資料庫、財務運算 |
| 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 | 資料工程、資料模式與知識探索、智慧型決策支援系統、人工智慧專題、管理資訊系統專題、群集智慧、高等資料庫、財務運算、網頁擷取程式設計 |
[表2-1-10]:碩士班與碩士在職專班「資訊系統開發與應用」模組課程之學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備資訊系統與管理之研究與管理能力 說明:學生需具備資訊系統的開發與應用的能力,其中軟體工程、軟體評估模式、物件導向技術等課程在培養學生有效率開發資訊系統的能力,相關程式課程則是讓學生利用習得之技術實際開發資訊系統與軟體,以培養學生之實作能力。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能整合資訊應用相關理論與技能(能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能) | 物件導向技術、軟體工程實務、軟體評估模式、行動裝置程式設計技術、劇本式程式語言、人機互動系統、進階Java程式設計議題、網頁開發技術 |
| 能執行資訊應用相關研究(能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究) | 物件導向技術、軟體工程實務、軟體評估模式、行動裝置程式設計技術、人機互動系統、網頁開發技術 |
| 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 | 物件導向技術、軟體工程實務、行動裝置程式設計技術、劇本式程式語言、人機互動系統、進階Java程式設計議題、網頁開發技術 |
[表2-1-11]:碩士班與碩士在職專班「創新網路」模組課程之學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備網路與多媒體之研究與管理能力 說明:學生需對目前網際網路之技術有所了解,並能實際運用相關技術進行軟體或系統開發。其中,網路效能分析與模擬讓學生了解網路效能之評估,各種創新網路課程介紹各網路型態之通訊協定,各專題課程則讓學生學習相關創新網路上應用程式或系統開發之能力。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
|
能整合資訊應用相關理論與技能(能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能) |
網路效能分析與模擬、點對點網路、高速網路專題、網路管理技術、網路安全技術、無線網路技術、雲端網路技術、下一代網際網路技術、平行與分散式系統、分散式系統專題 |
| 能執行資訊應用相關研究(能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究) | 網路效能分析與模擬、高速網路專題、網路安全技術、無線網路技術、雲端網路技術、下一代網際網路技術、平行與分散式系統、分散式系統專題 |
| 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 | 點對點網路、網路管理技術 |
[表2-1-12]:碩士班與碩士在職專班「多媒體技術」模組課程之學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備網路與多媒體之研究與管理能力 說明:學生需要對於目前多媒體技術的發展趨勢進行瞭解,包含了電腦視覺、影像處理、圖像辨識、影像監控、多媒體資訊檢索等領域,並且能夠利用演算法、人工智慧作為工具解決多媒體技術管理與研究中所遇到的問題。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能整合資訊應用相關理論與技能(能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能) | 高等演算法、影像顯示訊號處理、電腦視覺系統、影像處理、圖像辨識、影像監控系統專題、智慧型系統設計專題、多媒體檢索、進階動畫製作 |
| 能執行資訊應用相關研究(能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究) | 高等演算法、影像顯示訊號處理、電腦視覺系統、影像處理、圖像辨識、影像監控系統專題、智慧型系統設計專題、多媒體檢索 |
| 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統 | 影像處理、圖像辨識、影像監控系統專題、智慧型系統設計專題、多媒體檢索、進階動畫製作 |
[表2-1-13]:碩士班與碩士在職專班「數位學習」模組課程之學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備學習與數位科技研究與管理能力 說明:為了因應當前以學習者為本位的教學形態並且瞭解數位科技應用在學習上的趨勢,學生除了要擁有認知、動機與數位學習和研究等相關理論知識外,也應具備資訊融入教學、網路資源利用以及數位教材開發、管理與評鑑等實務知識與技能。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
|
能整合資訊應用相關理論與技能(能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能) |
數位學習導論、研究方法、學習理論與教學設計、網路資源利用、學習與認知、資訊融入教學理論與應用、學習動機與數位科技、數位內容評鑑研究、教育統計學、教學多媒體設計與製作、教學動畫製作 |
| 能執行資訊應用相關研究(能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究) | 數位學習導論、研究方法、網路資源利用、學習與認知、資訊融入教學理論與應用、學習動機與數位科技、數位內容評鑑研究、教育統計學 |
| 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統或數位教材 | 學習理論與教學設計、資訊融入教學理論與應用教學多媒體設計與製作、教學動畫製作 |
[表2-1-14]:碩士班與碩士在職專班「電子化政府」模組課程之學習成效指標與課程關聯表
|
專業/核心能力:具備學習與數位科技研究與管理能力 說明:學生需要對於電子化政府資訊應用發展的趨勢和議題研究瞭解,包括組織績效、知識管理、資訊策略規劃、資訊專案管理、資訊整合、資訊安全、人力資源管理等,並且養成推動與發展電子化政府的能力。 |
|
| 學習成效指標 | 科目名稱 |
| 能整合資訊應用相關理論與技能(能整合資訊應用相關理論與實務工作技能) | 組織績效、知識管理、資訊策略規劃、資訊專案管理、資訊整合、資訊安全、電子化政府、人力資源管理 |
| 能執行資訊應用相關研究(能執行與實務工作相關的資訊應用研究) | 組織績效、知識管理、電子化政府、人力資源管理 |
| 能開發、管理與評鑑資訊系統或數位教材 | 資訊策略規劃、資訊專案管理、資訊整合、資訊安全、電子化政府 |
As mentioned above, in addition to the compulsory courses in the "Information Application Panel Discussion", the Master's and Master's in-service classes provide students with a variety of options and flexibility. Similar to the design mechanism of the bachelor's degree course, the module courses of the master's and master's in-service courses are also prepared by the module course convener and the full-time teachers with relevant expertise, and then sent to the departmental committee for approval. For the professional/core competencies and subject development process of the module courses of the master's degree program, please refer to the [C#-2-2] course meeting minutes and the master's and master's degrees in [Appendix 2-1-5]. For the in-service syllabus, as for the number of courses in each subject after the implementation of the modular course, please see [Appendix 2-1-6].
In addition to explaining the purpose of establishment, educational goals, professional/core competencies, course content and future career development potential through the faculty website, the department also uses Facebook, course manuals, departmental corridors and career links, and new students. Different media and methods such as conferences, basic presentations, special presentations, course surveys, and course maps will enhance students' understanding of the above information. For related information, please see [Appendix 2-1-7]. In addition, in the 103th academic year, the department conducted a survey on the professional/core competence recognition of the university, master's, and master's in-service students. The results of the questionnaires of the university (91 people answered) showed that the five-equivalent scale Among them, students believe that the average of the importance of each of the seven major/core competencies is higher than 3.5, and more than 60% of each professional/core competency is considered important or very important. The results of the master's class (15 respondents) show that in the five-equivalent scale, students believe that the average of the importance of the three major/core competencies is higher than 4.5, and each professional/core competency has More than 90% of respondents believe that it is important or very important. As for the master's in-service class (9 people answering), the average value of the three major/core competencies is higher than 4.2, and each professional/core competency has more than 75% of the respondents. Think it is important or very important. In addition, the Department's website, the course manual, and the syllabus and curriculum plan are the most commonly used by university students to understand the department's educational goals and professional/core competencies. Students in the Master's program most often use the "Information Application Discussion" course and the syllabus and curriculum plan, while the students in the Master's in-service class use the faculty website and syllabus and course plan to understand the department. The educational goals and professional/core competencies, and the questionnaire on the professional/core competence identity, please see [Appendix 2-1-8] and [Appendix 2-1-9].
In addition to explaining the purpose of establishment, educational goals, professional/core competencies, course content and future career development potential through the faculty website, the department also uses Facebook, course manuals, departmental corridors and career links, and new students. Different media and methods such as conferences, basic presentations, special presentations, course surveys, and course maps will enhance students' understanding of the above information. For related information, please see [Appendix 2-1-7]. In addition, in the 103th academic year, the department conducted a survey on the professional/core competence recognition of the university, master's, and master's in-service students. The results of the questionnaires of the university (91 people answered) showed that the five-equivalent scale Among them, students believe that the average of the importance of each of the seven major/core competencies is higher than 3.5, and more than 60% of each professional/core competency is considered important or very important. The results of the master's class (15 respondents) show that in the five-equivalent scale, students believe that the average of the importance of the three major/core competencies is higher than 4.5, and each professional/core competency has More than 90% of respondents believe that it is important or very important. As for the master's in-service class (9 people answering), the average value of the three major/core competencies is higher than 4.2, and each professional/core competency has more than 75% of the respondents. Think it is important or very important. In addition, the Department's website, the course manual, and the syllabus and curriculum plan are the most commonly used by university students to understand the department's educational goals and professional/core competencies. Students in the Master's program most often use the "Information Application Discussion" course and the syllabus and curriculum plan, while the students in the Master's in-service class use the faculty website and syllabus and course plan to understand the department. The educational goals and professional/core competencies, and the questionnaire on the professional/core competence identity, please see [Appendix 2-1-8] and [Appendix 2-1-9].
The Department has the following three advantages in the development of educational goals, core competencies and curriculum planning: (1) The educational goals of the department are closely related to the orientation and development direction of the school and the hospital. In addition, this The educational goals of the department are clear, and it also meets the needs of the professional development and employment market, and considers the characteristics and faculty conditions expected to enroll students. (2) The department expects to develop the professional/core competencies of the students, and all have corresponding courses or Module courses and learning effectiveness indicators to help achieve goals and review their achievement; (3) The curriculum design of the department has a learning logic, from basic introduction, advanced to integrated application, and allows students to freely and adaptively Self-exploration and career preparation.
Affected by the economic downturn, the lack of children and the competition of other departments, the biggest difficulty encountered by the department is that the enrollment and enrollment status of the master's and master's in-service classes is difficult to master, which will affect the diversity of the course more or less.
With regard to the enrollment of the master's degree program, the department has fully cooperated with the enrollment policy of the school and hopes to develop more actively by providing modular courses, sending enrollment posters, brochures, emails, workshops, seminars and speeches, and alumni recommendation. Sources of students in Keelung, New Taipei City, Taipei City and Taoyuan County. In order to encourage students with outstanding academic performance in the university to continue their studies, the master's degree program from the second semester of the 103th school year will be set up with a substantial incentive of 70,000 yuan. The department also actively considers the establishment of master's degree classes and corporate classes to gradually guide students into master's or master's in-service special classes.
Overall, the department still has room for improvement in terms of educational goals, professional/core competencies and courses. However, there are already well-planned plans. In addition to the participation of all full-time teachers in the process of development, this The professional/core competencies of the department are also recognized by most students. As for the problems encountered, the department has developed countermeasures and will continue to identify and solve problems through self-assessment organization and operational mechanisms.